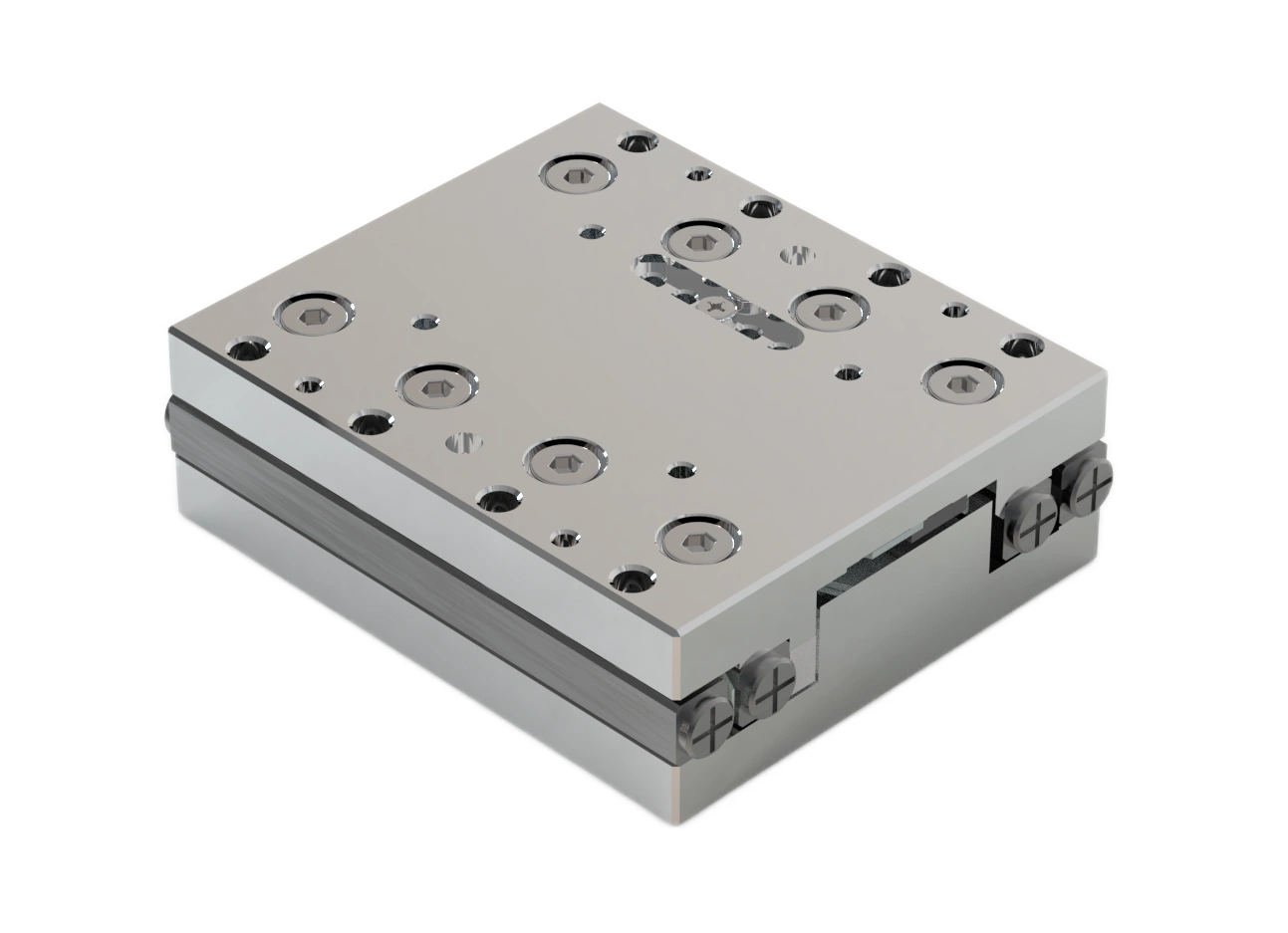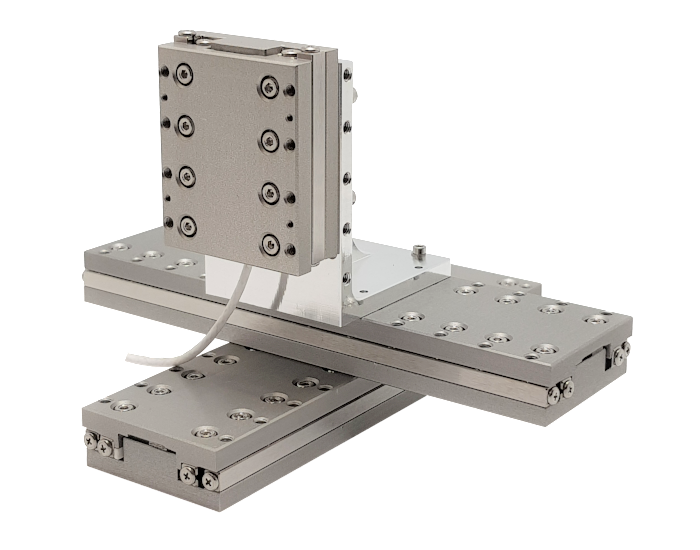
Crossfixx™ piezo motor
Piezo motors do not have to be slow, loud and expensive
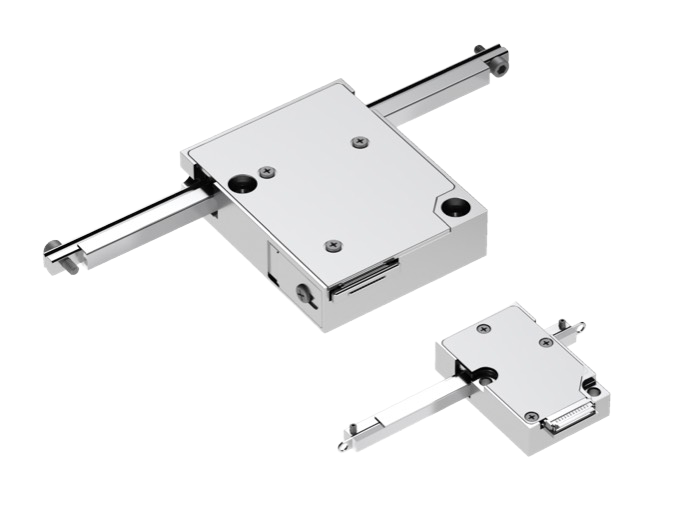
Xeryon's patented Crossfixx™ ultrasonic piezo motor is the backbone of all of our motion products.
It marks a breakthrough in motion control, as it offers all of the advantages of piezo technology without the drawbacks typically associated with it.
Combining speed, precision, range and power with durable, silent operation, the compact Crossfixx™ motor is a superior alternative to many types of miniature motors currently available.
Resonant piezo technology
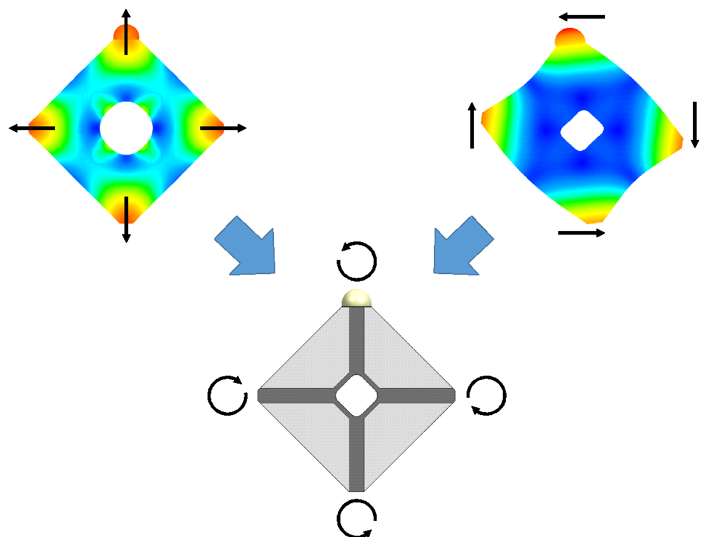
Xeryon’s patented Crossfixx™ motor is based on 2 resonant modes with coincident resonant frequencies.
The first mode produces a uniform radial expansion of the piezoceramic in which the contact point vibrates perpendicularly to the stage.
The second mode is characterized by in-plane bending with the contact point vibrating parallel to the stage.
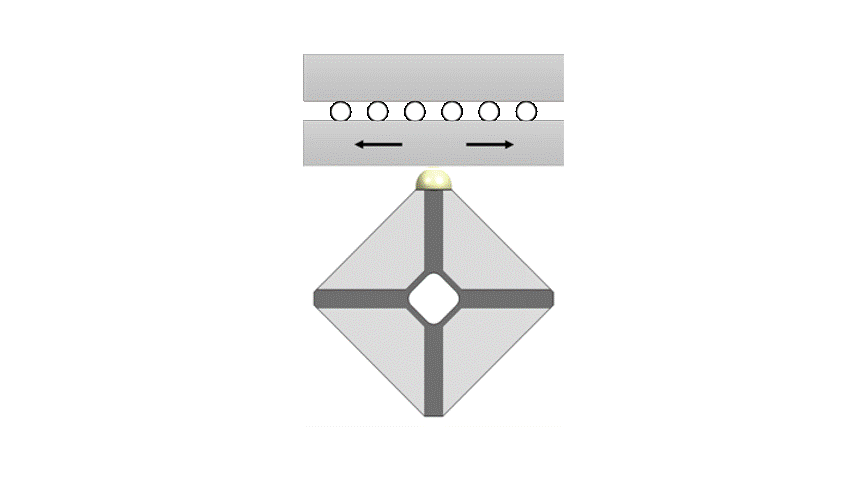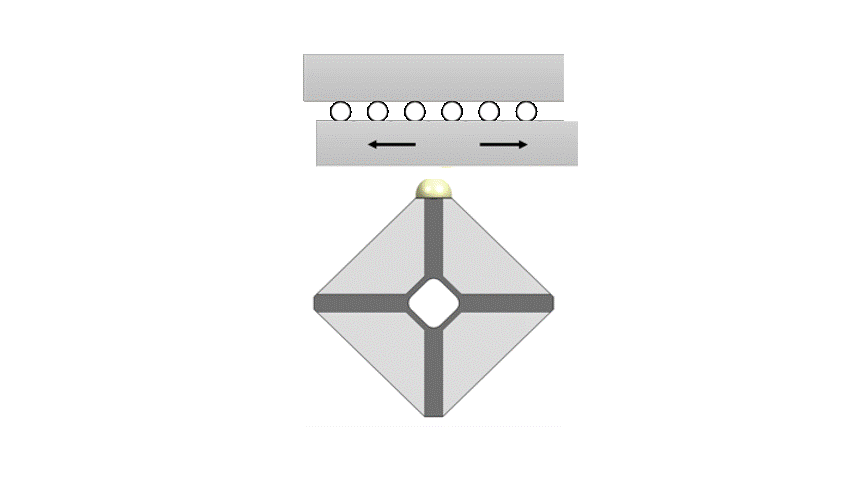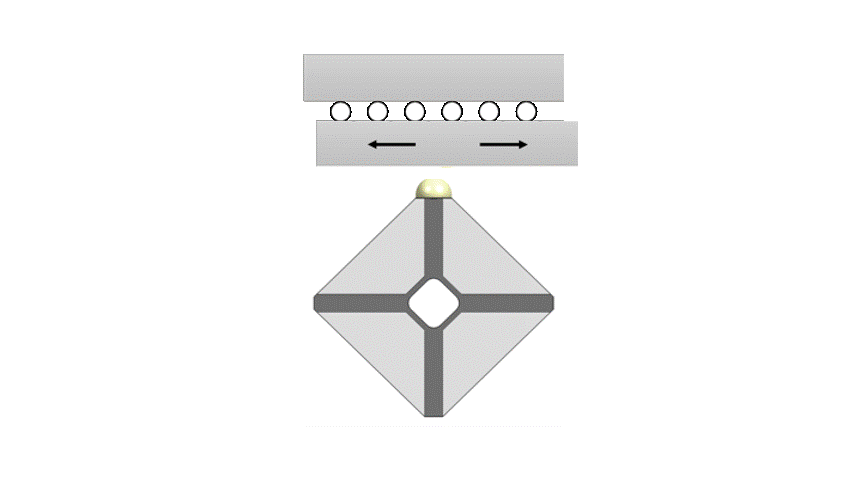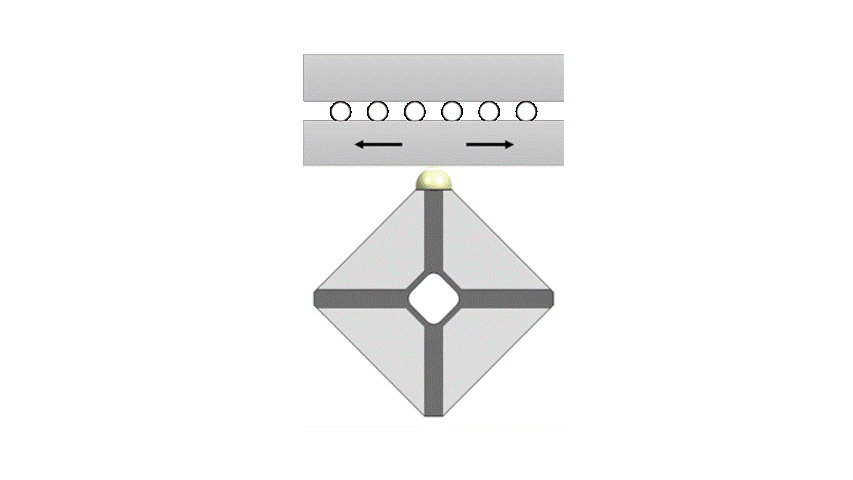
By combining both modes the tip of the motor will follow an elliptical path. The displacements of the vibrating tip are small, order of magnitude 1 µm, but as this elliptical motion repeats itself at 166 kHz, speeds up to 1000 mm/s can be obtained.
Advantages of ultrasonic operation
The motor resonates at 166 kHz, well above the audible limit of the human ear. Therefore, the motor can operate silently.
166 kHz is also well above the cutoff frequency of most mechanical systems such that mechanical disturbance of the surrounding mechanical systems is negligible.
Resonant operation also brings down the excitation voltages to safe limits. Operational voltages as low as 20 V are possible, while for more demanding applications voltage can be increased to 48 V.
Fixation
The motor is fixed in the center hole which is a nodal point for both modes. This has a number of advantages:
-
The motor transmits no vibrations via this fixation point towards the environment
-
Minimal influence of the fixation on the modes and corresponding resonant frequencies
-
Symmetric fixation, reducing thermal drift
-
Compact fixation
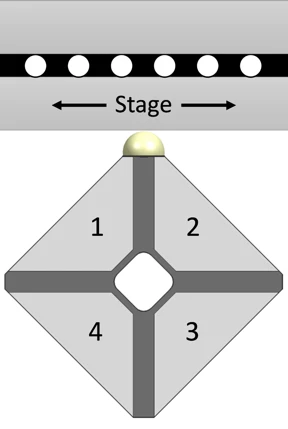
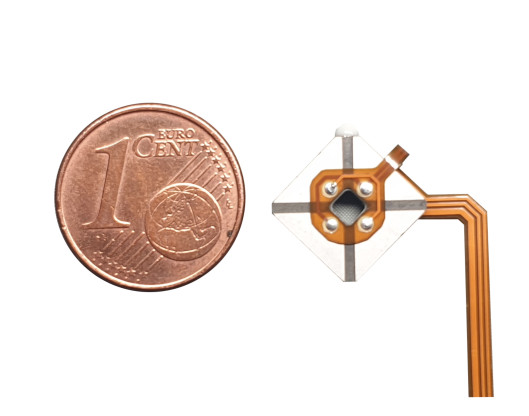
Motor phase 1: electrodes 1 & 3
Motor phase 2: electrodes 2 & 4
Controlling the Crossfixx™ motor
The motor has 4 electrodes on the front and 1 common electrode on the back. The electrodes on one diagonal form one motor phase, those on the other diagonal the second motor phase. Applying the same sinusoidal signal to both motor phases will excite the 4 quadrants of the motor equally and therefore excite the expansion mode.
When exciting the electrodes on one diagonal 180 degrees out of phase with the electrodes on the other diagonal, the bending mode is excited. Phase differences of 90 degrees excite both modes and let the tip follow an elliptical trajectory. By playing with the amplitude and phase difference, the shape and size of the ellipse can be changed, influencing the driving force and speed of the motor.
Generation of these excitation signals is done by Xeryon’s controller. The user only must specify basic input variables such as desired speed or position and the controller will adapt the excitation signals accordingly to achieve these goals.